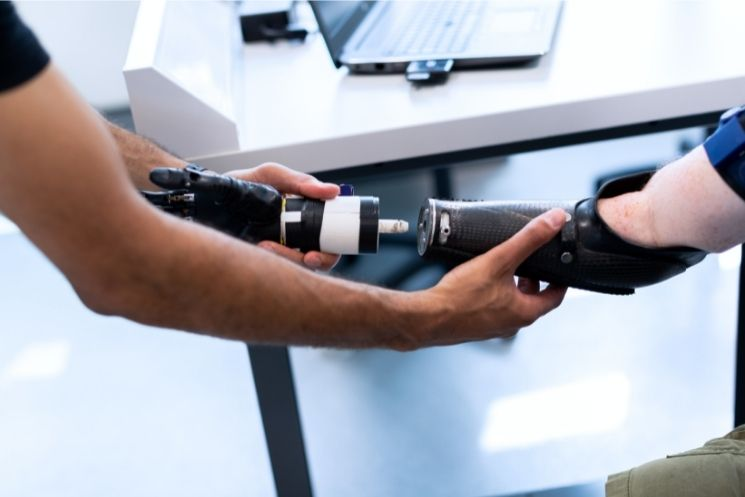
Robots are not things of the future anymore and it won’t be long until robots and Automated Robotic Systems become an inseparable and integral part of our day-to-day lives.
From doing everyday chores like driving people to places, to simplifying medical procedures and manufacturing and assembling components in a factory, the potential of robots and robotic systems has no limit.
In the manufacturing and fabrication industries, robots and industrial robotic systems have huge applications. The level of precision that can be obtained by using robotic systems in manufacturing is very high, and the same results cannot be obtained from manual operation.
This blog provides an overview of origins and development of robots and robotic systems, and the manufacturing applications of robots.

WHAT IS A ROBOT?
A robot is a machine built for replicating certain functions precisely and efficiently, which is usually tedious for humans. It is designed to perform specific tasks by reducing human effort, either through remote control or through the use of automated computer commands. Robotics is the study of robots, which includes the design, ideation, creation, and operation of robots.
Any automated machine that performs a task by eliminating human effort, even though the appearance and function may not resemble human beings, is by definition a robot.

HISTORY AND ORIGIN OF ROBOTS
It is uncertain who created the world’s first robot. However, perhaps the most popular fictional robots were modeled after their ancient counterparts—human-made machines designed to serve and obey their human creators.
The idea of “man-made” humans has been recorded in historical texts. But the term “robot” is derived from the Czech word robota, meaning “forced labor”. Another citation can be seen in ancient Greek texts, where the idea of creating artificial servants was considered the pinnacle of craftsmanship and inventiveness.
The first-ever patent for an industrial robot was filed in 1954 by the inventor George Devol. The prototype model of his design was created in 1961. His design functioned much like today’s robotic arm. It was able to carry 500 pounds and perform human tasks with quiet ease.
The evolution of modern robots has been ongoing for decades. From large machines, often seen in science fiction, to smaller, more agile robots designed to perform intricate tasks and to serve special purposes, robots have become an integral part of our lives.

They help in completing everyday processes by working alongside humans in various industries. With rapid technological advancements, it’s hard to predict what the future holds for industrial robots.
USAGE IN MANUFACTURING: INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
An industrial robot is a type of robot that is designed for manufacturing applications. They are automated and computer programmable robots that usually have a multi-axis movement to perform manufacturing and fabrication-related tasks. There are many types of robots that fall into this category.
Such robots are typically used to automate certain stages of fabrication and manufacturing, such as welding, assembling, painting, packaging, labeling, and so on. Such robots can perform the aforementioned tasks more efficiently and with greater precision and higher speed than human workers.

Apart from such industrial robots, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has become a vital part of On-Demand manufacturing projects. RPA is a means of automating a manufacturing process by using automation software that can operate machines and other robots involved in the manufacturing process, to perform tasks and operations more efficiently and in a streamlined manner.
Along with reducing the cost of production, it also eliminates bottlenecks that could potentially damage or delay products.
The modern approach to RPA uses applications such as Red Cap Insight to examine a production line’s current activities and identify potential problems that an employee might encounter. It helps in optimizing efficiency.
TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
To meet the increasing rise in demand for products in the market, manufacturers are shifting more towards the automation of various manufacturing processes. As robots and automated systems can perform repetitive tasks more effectively and quickly than human workers, different processes in the manufacturing cycle can be automated by using different types of robots.
The robots used in the manufacturing industries can be classified into 4 major categories:

1. ARTICULATED ROBOTS
Articulated Robots are the premier group of industrial robots that are used in the manufacturing industries. These robots are extensively used in the industries owing to their design and versatility. The most common type of articulated robot is the 6 axes articulated robot.
Articulated robots are categorized by the number of points of movement that the robot has. As the 6 axis robot has six joints, leading to 6 axes of linear or rotational motion, these robots can be configured to perform various tasks.
Some common operations that these robots are used for are welding, assembly, packaging, inspection, dispensing, and so on. The elementary design of all articulated robots is the same and the only difference is in the configuration and other operational attachments made to the robot structure.

2. SCARA ROBOTS
SCARA stands for Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm. These are lightweight robots with a fixed arm design and a small footprint. These robots are excellent for performing operations that are repetitive and do not require much movement of the robot, such as assembly of small and intricate parts.
SCARA robots can also be programmed to operate in high-speed cycles, as the frame of the robot is stationary. These robots are specially used for the assembly of parts with tight tolerances, such as jigs and fixtures.

3. CARTESIAN ROBOTS
Cartesian robots are frame-mounted arms that can be positioned by inputting cartesian coordinates of the position where the arm of the robot is required for operation. Cartesian robots consist of actuators that move linearly and also rotate, giving the robot arms a wide range of motion.
The robot can also be suspended on an elevated frame over railings for linear movement. This particular arrangement of cartesian robots is known as Gantry robots and they are extensively used for pick and place operations and also in the assembly line of various products.
4. DELTA ROBOTS
Delta robots consist of three actuated arms connected to a universal joint converging the three arms to a single point. The arms are suspended down from the robot body with each arm connected to a motor inside the robot body. The motors coordinate and help in the movement of the robotic arms, in both up-down and forward-backward positions.
As the robot arms are made of lightweight materials and the overhanging robot body is stationary, delta robots can be used for high-speed operations such as quick assembly of delicate parts, sorting, pick and place operations, and so on.
The advantage of delta robots over other types of robotic arms is the design of the robot. As the motors of the robotic arms are located in a single body, rather than being placed on the arm itself, it reduces the weight on the robot arms making them more agile in operation.
Thus the potential for robots in the manufacturing industry is very high and there are many applications where robots can be used.
PRODUCTION OF ROBOTS
Over the decades, scientific developments in manufacturing and increases in demands have made the production of robots more efficient, while greatly cutting down the cost. Developments in robotic design have led to the creation of robots for different types of industrial applications.
Mechanical robotic arms have become very common in automotive factories and other manufacturing plants. Along with these, there are collaborative robots that work in tandem with human shop-floor workers.
All this has been possible because of the technological advancements in manufacturing science and material technology. The advancements in CNC manufacturing technology and 3D printing have made it possible to create robots more efficiently and by using composite materials, as opposed to the traditional manufacturing approach.
CNC machines and 3D printers can be used separately or simultaneously to cut complex parts for robots or print more durable parts. Depending on the type of robot to be manufactured, the complexity of the design will vary.
Thus CNC machining and 3D printing can be used extensively for creating high complexity robots for special purpose applications.
CNC machines offer rapid prototyping, and the programs are easy to configure. 3D printing solutions have increased machine efficiency over three dimensions.
Thus robotic design structures can be manufactured more efficiently and more economically by creating individual components using CNC machining and 3D printing.
CONCLUSION
To meet the ever-increasing demands of the market, it is important to increase the pace as well as the volume of manufacturing. One of the ways of achieving this is by incorporating robotics and automated systems into the manufacturing cycle.
Many repetitive jobs can be performed more efficiently and effectively if robotic systems are used to automate these processes. This would not only save a lot of time by streamlining such tasks but also increase the overall efficiency of manufacturing by making the production cycle smaller and faster.
With technological advancements in manufacturing science, there is a lot of scope for robotics in manufacturing. Different processes in a manufacturing cycle can be performed more effectively by automation, and special robots can be designed to suit the needs of different industries.
More research must be made in the field of robotics, as well as manufacturing to know more about the capabilities of such machines and how they can be incorporated more in the manufacturing industries.
Karkhana for your robot manufacturing needs
Karkhana.io is a flexible & scalable manufacturing solutions provider that can cater to all your manufacturing needs in Robotics.
Our flexible manufacturing services enable us to service client orders of all sizes from small batches to large volumes. We also help many of our clients in solving complex product assembly and localization problems.
We have an extensive, cutting-edge experience with all manufacturing services like CNC machining, 3d printing, Sheet metal fabrication, Injection moulding, and Vacuum casting.
We cater to every manufacturing need across industries like Aerospace, Automation, Automobile, Defence, Drone, Energy, EVs, FMCG, General Engineering, Medical, Oil & Gas, Pharma, and Robotics.
Partner with us to bring speed to your manufacturing. Talk to us about your manufacturing needs by filling up the form below or get in touch with Alay at alay@karkhana.io